Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-04-25 Origin: Site











In today’s industrial landscape, the diesel generator remains a core component for reliable power supply. However, growing concerns over noise pollution and emissions have prompted manufacturers to innovate at the design level to reduce their environmental impact.
Low-noise design is now an industry standard. This includes the use of high-density acoustic insulation, multi-stage mufflers, and optimized airflow paths. Spiral or labyrinth exhaust structures can absorb turbulence-induced sound, while double-layer enclosures drastically reduce operating decibel levels.
On the emissions side, combustion system optimization plays a pivotal role. Advanced common rail injection systems allow for precise fuel delivery, resulting in cleaner combustion and fewer unburned particulates. Technologies like exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) and diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC) also reduce NOx and CO emissions to meet standards such as Euro V or EPA Tier 4.
Efficient air filtration systems further support clean combustion. In dusty industrial environments, dual-stage filtration and precision intake management ensure that only clean air reaches the combustion chamber, reducing soot formation and prolonging engine life.
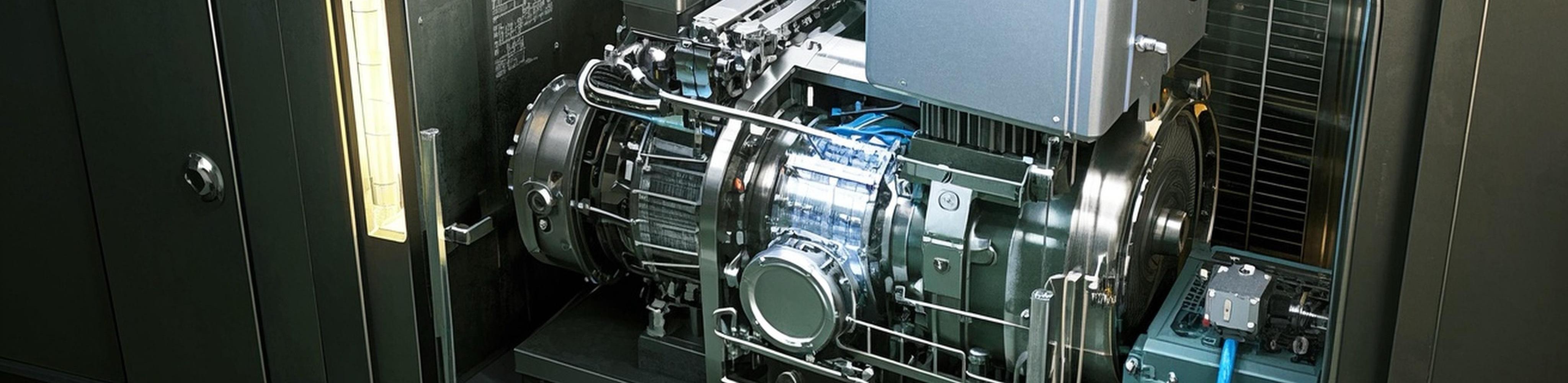
Complementing internal improvements, external auxiliary systems play a vital role in minimizing environmental impact. The soundproof enclosure is the most direct noise control measure. With integrated acoustic layers, it reduces noise to as low as 70 dB—ideal for hospitals, residential zones, and public spaces.
Exhaust silencers reshape acoustic waves to suppress engine noise. Depending on application, industrial generators may use hospital-grade, residential-grade, or industrial-grade silencers to meet different standards.
To manage emissions, after-treatment systems are widely implemented, including:
DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst) to reduce carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons
DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) to trap and regenerate soot particles
SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) to convert NOx into harmless nitrogen and water using urea injection
Together, these systems can achieve pollutant reduction levels above 90%, ensuring regulatory compliance even in strict markets.
Modern generators are increasingly equipped with intelligent monitoring systems that track real-time emissions and acoustic data. These systems transmit data to cloud platforms and generate alerts when thresholds are exceeded, helping companies stay compliant and avoid fines.
As part of the global push for sustainability, businesses are adopting green energy alternatives to diesel. Biodiesel generators and hybrid systems combining solar, battery storage, and diesel allow for dynamic power delivery, reducing run time and emissions.

Some enterprises also invest in carbon capture technologies or participate in offset programs to neutralize their carbon footprint. Procurement strategies now prioritize suppliers with ISO environmental certifications, lifecycle assessments (LCA), and recyclable component designs.