Views: 6 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-04-30 Origin: Site











A portable generator is a self-contained unit designed to produce electricity wherever and whenever it is needed. Most commonly used during power outages, in construction sites, or for outdoor activities, portable generators play a vital role in emergency and off-grid power supply. At the heart of many reliable models lies the diesel generator, prized for its durability, fuel efficiency, and high power output.
But how exactly does a portable generator convert fuel into electricity?
The core components of a portable diesel generator include a diesel engine, alternator, fuel system, cooling and exhaust system, lubrication system, and control panel. The diesel engine combusts fuel to create mechanical energy. This energy is then transferred to the alternator, which converts it into usable electrical energy via electromagnetic induction.
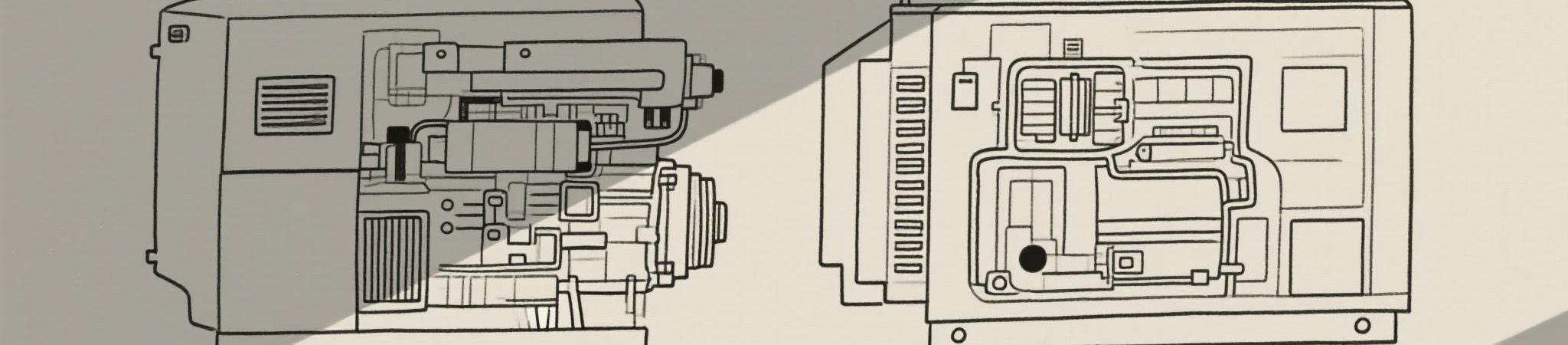
The alternator consists of a rotor (moving part) and stator (stationary part). As the rotor spins inside the stator, it creates a magnetic field that generates an electrical current. This current is then regulated and distributed to connected appliances or circuits through the generator’s control panel.
Unlike permanent standby generators, portable diesel generators are often air-cooled and manually operated. They come in various sizes and power ratings, often between 1kW and 10kW, although heavy-duty portable models can exceed 20kW.
The efficiency of diesel combustion, combined with the generator’s ability to maintain stable voltage and frequency output, makes these units suitable for sensitive electronics, lighting, power tools, and backup loads.
Understanding the internal systems of a portable generator offers insight into how it runs efficiently and safely for extended periods. Let’s break down the major components:
Diesel Engine
This is the powerhouse of the unit. Diesel engines are preferred due to their high compression ratio, which leads to better fuel efficiency and longer engine life. A properly maintained diesel engine can run for thousands of hours without issue.
Alternator
This component converts mechanical rotation into electrical energy. It’s built with copper windings and high-quality insulation to handle long operational hours and fluctuating loads. In most industrial generators, brushless alternators are used for lower maintenance.
Control Panel
This allows the user to monitor voltage, frequency, engine hours, and fuel level. Some advanced models come with remote monitoring systems, digital meters, and automatic shutdown features in case of faults.
Fuel System
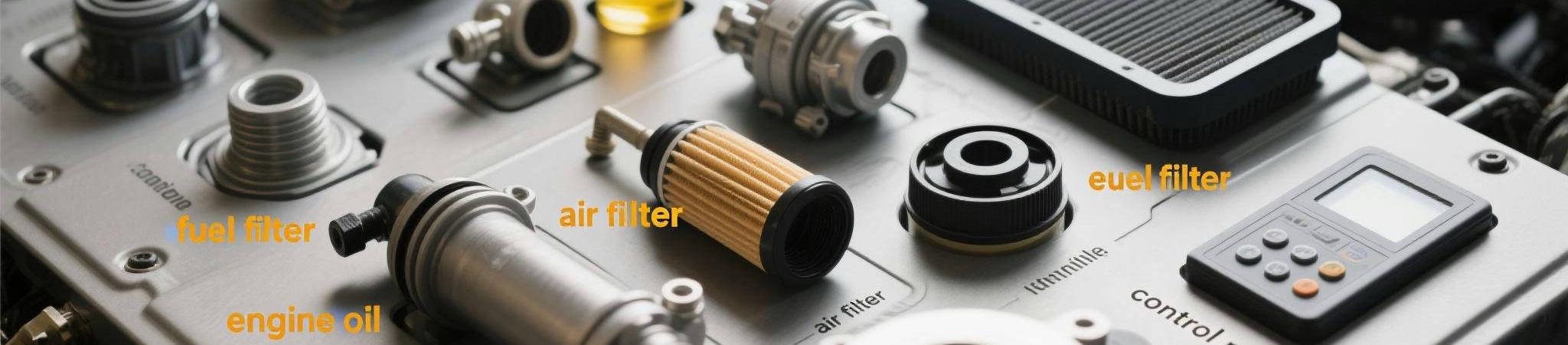
A typical portable diesel generator includes a built-in fuel tank capable of running the unit for several hours. Fuel lines, filters, and injection pumps are engineered to ensure efficient combustion. Maintaining clean fuel and replacing the fuel filter regularly is critical.
Cooling System
Smaller portable generators are air-cooled, while larger units might use a radiator and fan. Overheating protection is essential for longevity and performance.
Exhaust and Emissions Control
Diesel engines emit carbon monoxide and particulates, making proper exhaust venting vital. Always operate portable units outdoors or in well-ventilated areas and consider attaching a carbon monoxide detector indoors for safety.
Lubrication System
To prevent friction damage, engine components are lubricated with oil. Regularly changing engine oil and replacing the oil filter helps preserve generator performance.
Each component must work harmoniously. Any failure in the air filter, fuel injection, or voltage regulation system can lead to inefficient power production or even total breakdown.

Portable generators, especially diesel models, have become essential tools for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. From camping trips to disaster response, their portability and reliability make them indispensable in many settings.
Key applications include:
Home backup power during grid outages
Powering construction tools on remote job sites
Supporting mobile medical clinics
Running food trucks and outdoor events
Supplying electricity to mining camps or agricultural equipment

To ensure optimal use, follow these best practices:
Proper Load Management
Know your generator’s rated capacity. Use watt meters or calculate the combined wattage of all devices you plan to run. Always prioritize essential equipment and avoid overloading.
Safety First
Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces. Use weatherproof covers and ensure proper grounding through a grounding system to avoid electrical shocks.
Routine Maintenance
Regularly inspect for oil leaks, loose bolts, or air blockages. Replace consumables such as air filters, fuel filters, and engine oil according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Smart Storage
If not in use for long periods, drain the fuel or use stabilizers to prevent fuel degradation. Store the unit in a dry, secure place.
Compliance with Local Regulations
In some areas, emissions standards and noise regulations apply even to portable units. Select models with low noise ratings and emission controls if used in urban or regulated zones.
Ultimately, understanding how a diesel generator works—from engine combustion to alternating current delivery—empowers users to operate these machines safely and confidently in any scenario. Whether for short-term outages or long-haul projects, a portable diesel generator is a reliable ally in energy resilience.