Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-04-25 Origin: Site











For beginners entering the industrial power field, installing and operating a diesel generator requires more than just plugging in a machine. It involves understanding critical factors such as power sizing, installation environment, and regulatory compliance to ensure both safety and long-term performance.
When selecting a generator, matching the rated power with the facility’s load demand is vital. Undersized units may overload and fail; oversized units increase capital and fuel costs.
Proper installation conditions must also be met. The unit should be placed on a level, ventilated site, away from heat, moisture, and corrosive elements. Outdoor installations should use a weatherproof canopy or soundproof enclosure to protect against environmental stressors.
Before commissioning, check that grounding is adequate, exhaust is properly routed, the fuel system is sealed, and all electrical and emission regulations are followed. This ensures safety and avoids penalties from inspections.
New users must familiarize themselves with operation procedures, system alerts, and routine maintenance. Key practices include:
Start-up and Shutdown Procedures
Always inspect fluids and battery voltage before starting. Monitor parameters like oil pressure and voltage after start-up. Run the unit on no-load briefly before shutting down to cool components.
Monitoring and Fault Alerts
Digital control panels provide real-time status and automatically shut down during issues like low oil pressure or high engine temperature. Learn how to read and respond to alarm codes.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regularly replace oil and filters, test the battery, check fuel lines, and tighten electrical connections. Conduct primary maintenance every 250 hours and more thorough service every 500 hours.
Spare Parts and Emergency Tools
Keep essential spares (filters, fuses, belts) on hand. Stock emergency gear such as fire extinguishers, multimeters, and manual tools—especially important in remote deployments.

These practices help extend the generator’s life, reduce downtime, and cut costs.
Modern tools and digital solutions make it easier for beginners to operate and manage generators efficiently:
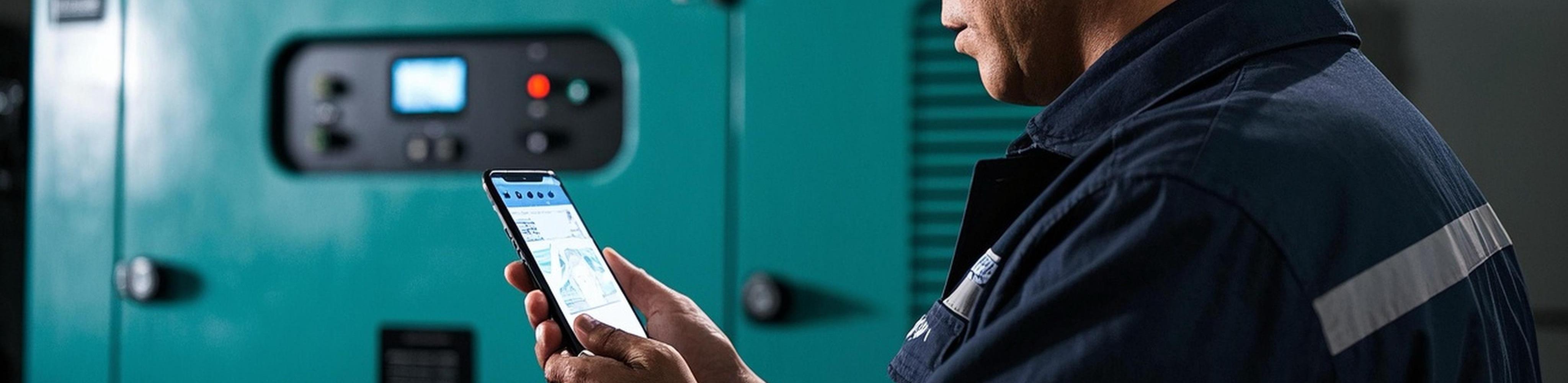
Remote Monitoring Systems
Access real-time data and perform remote diagnostics via cloud dashboards or mobile apps, ideal for unstaffed sites.
Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS)
Ensure seamless power supply by automatically starting the generator during grid failure and stopping it once power is restored.

Installation Support Tools
Use AR apps or video guides provided by manufacturers to learn wiring, grounding, and exhaust connections with step-by-step visuals.
Cloud-Based Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
AI-powered analytics help detect patterns, predict failures, and schedule preventive maintenance proactively.
By understanding and applying these principles, beginners can ensure safe, effective, and long-lasting use of industrial generators.